In a recent blog, DeNexus' Head of Research and Modeling, Romy Rodriguez Ravines discussed the challenges of Cyber Risk Aggregation and DeNexus’ unique bottom-up approach powered by Inside-Out data to accurately quantify, model, and estimate portfolio-level cyber risk with our flagship product DeRISK, the leading AI/ML powered, evidence-based, data-driven, OT/ICS Cyber Risk Quantification and Management platform.
In this blog, DeNexus Risk Modeler, Diana Carrera elaborates on the significance of Co-Exposure, Inside-Out Data, and Risk Accumulation.
In cyber risk, a cyber-attack can result in claims that erupt across the globe, and financial loss events can be very nuanced and complex. Furthermore, systemic risk, a pivotal concept in cyber risk aggregation, is characterized by the potential for a single incident to unleash a cascading failure, ultimately precipitating the collapse of an entire system. An illustrative example would be a cyberattack that disables the power grid, thereby impacting sectors ranging from transportation to communications and healthcare.
The ever-changing nature of cyber threats, combined with intricate dependencies and limited data availability, intensifies the challenges within the cyber risk management landscape.
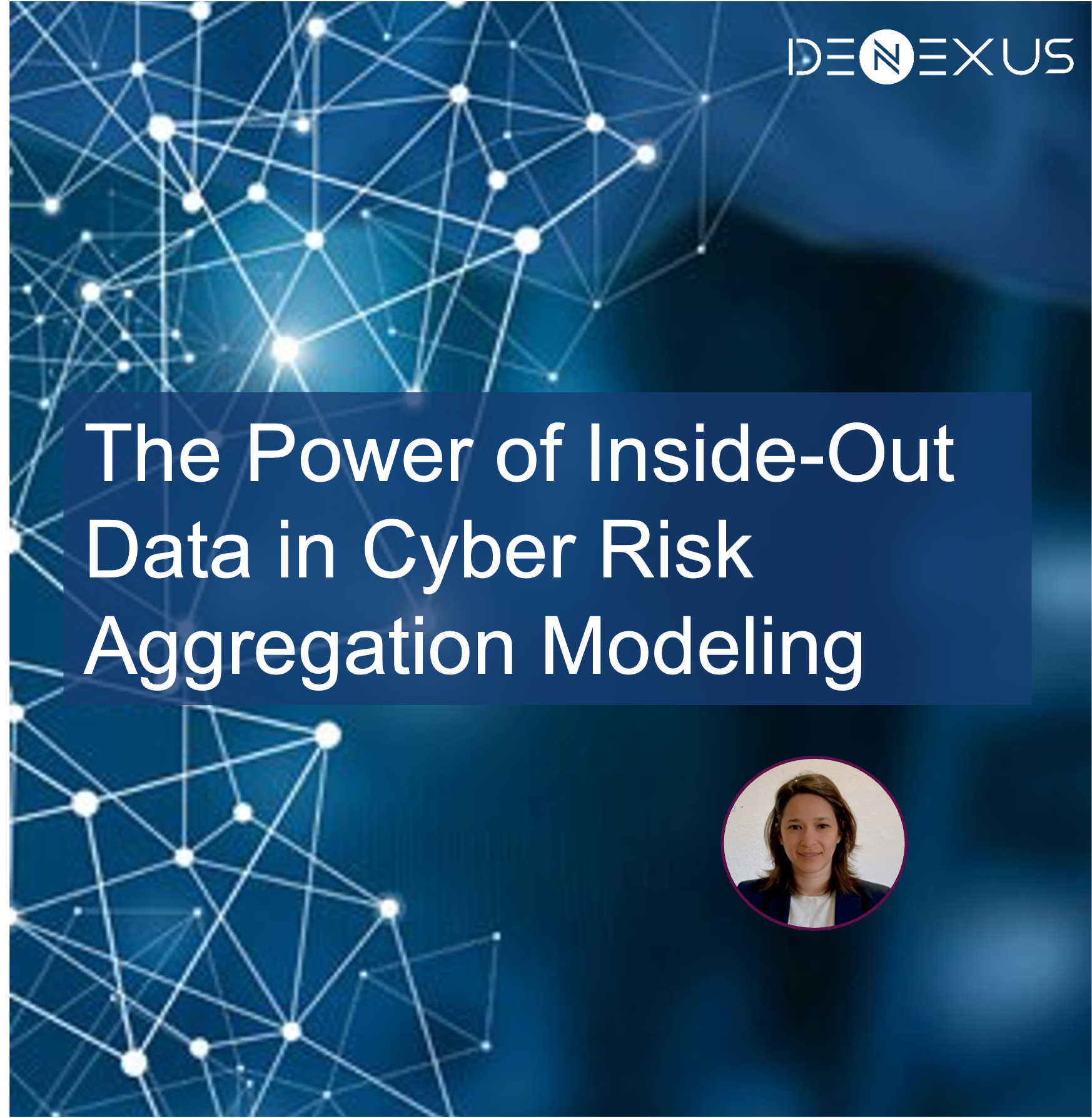
DeNexus' differentiator is its unparalleled access to invaluable inside-out data from facilities/unit risks, making it a foundational aspect of its prominence in the cyber risk accumulation field.
DeNexus' unique dataset, the DeNexus Knowledge Center, fuses real facility insights with simulations, bridging the domains of cybersecurity, risk management expertise, and advanced statistical modeling.
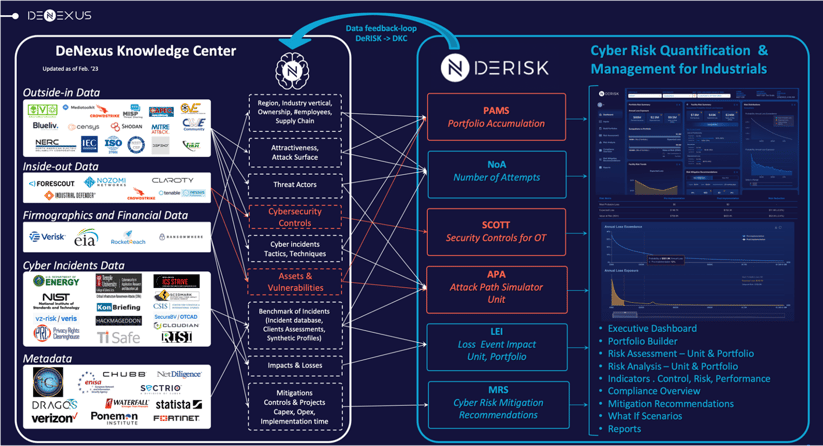
The significance of Co-Exposure and risk accumulation
Understanding Cyber Risk Accumulation is vital, especially with the interconnected nature of different units facilities, both physical and digital. Co-Exposure describes the shared risks faced by multiple facilities, and it must be considered to properly model the risk, enabling powerful bottom-up cyber risk aggregation modeling powered by Inside-data, that combined with traditional top-down powered by outside-data produces best-in-class cyber risk quantification at the Portfolio level, facilitating efficient evidence-based, data-driven, ROI-optimized risk management.
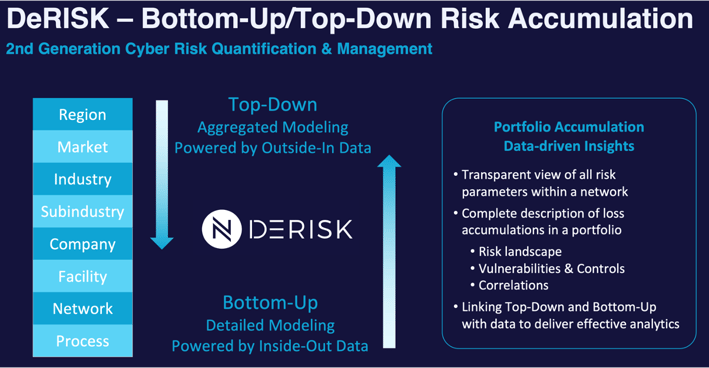
Systemic Cyber Risk can lead to widespread failures across multiple sectors, emphasizing the importance of powerful modeling tools to capture these intricate dependencies. That’s what we do at DeNexus with DeRISK.
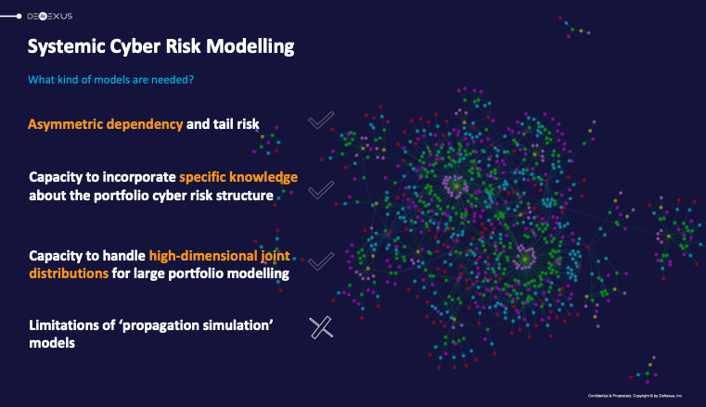
Vine-copula models and their benefits
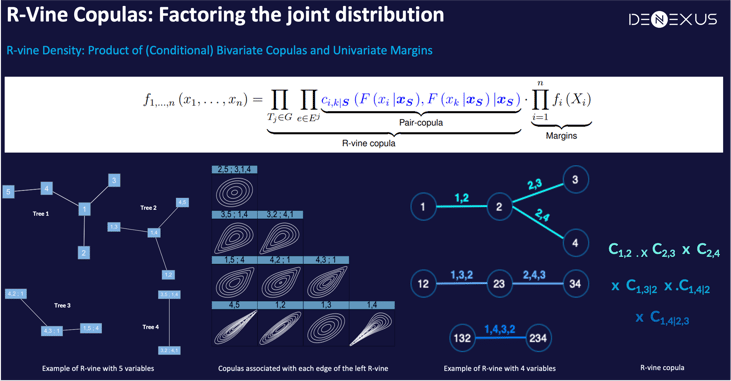
At the core of DeNexus’ approach lies the use of regular vine-copulas (R-vines). These models factorize joint distributions, effectively capturing the intricate inter-dependencies within a Portfolio of facilities.
Leveraging that critical inside-out data unlocks the potential for true modeling of the Co-Exposure between different facilities within a Portfolio.
Something simply not-possible without that Inside-data that characterizes the underlying networks, assets running on them, vulnerabilities living in those assets, controls deployed to mitigate the risk around them, and how different facilities relate to each other, physically and digitally
Notably, the R-vine structure is elegantly represented through nested trees (R-vine graph), where each node symbolizes a random variable and the edges signify the dependencies between them, thereby visually encapsulating the complex relationships within the model. The structure of the R-vine, with its sequence of conditional bivariate copulas, provides a refined method to capture all these diverse types of dependencies within a single model, enabling DeRISK to operate on a class of its own.
DeRISK: Modeling process and strategy
The modeling process begins defining a specific Portfolio and meticulously gathering inside-out and outside-in data related to facility characteristics, its owner, operators, etc. All that data lives in the DeNexus Knowledge Center, carefully stored with all cybersecurity best practices in place (read more on DeNexus Trust Center).
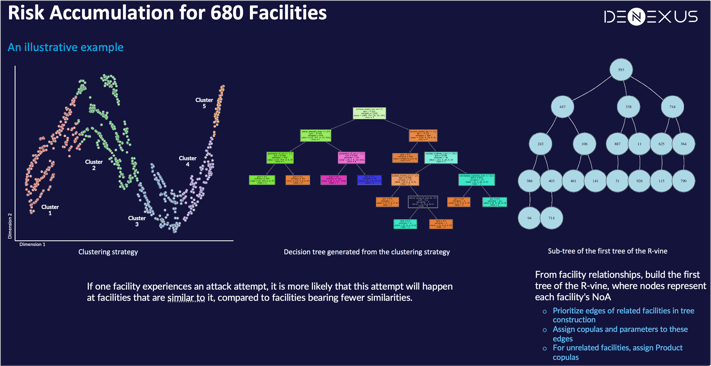
Machine Learning techniques are then applied to identify facilities with similar risk characteristics. This ensures that the model accurately reflects real-world Risk Accumulation scenarios. It is noteworthy that facilities with closely aligned characteristics are more prone to concurrent risks.
In the development of the vine-copula model, another module in DeRISK, the Number of Attempts Module -NoA- calculates the number of times that a customer/owner/facility will be attacked, and values for each facility serve as nodes in the R-vine graph model. Edges between these nodes are drawn to emphasize facilities with shared characteristics. Based on the degree of relatedness, appropriate pair-copulas are assigned to these edges.
The power of inside-out data
Through the simulation of the R-vine model and the subsequent translation of this data into NoA values, DeNexus provides an in-depth understanding of the Co-Exposure dynamics among interconnected facilities within the same Portfolio.
Comparative insights
Comparing independent NoA models with the R-vine NoA models, the latter offer more accurate projections of potential losses, highlighting the importance of understanding inter-facility relationships.
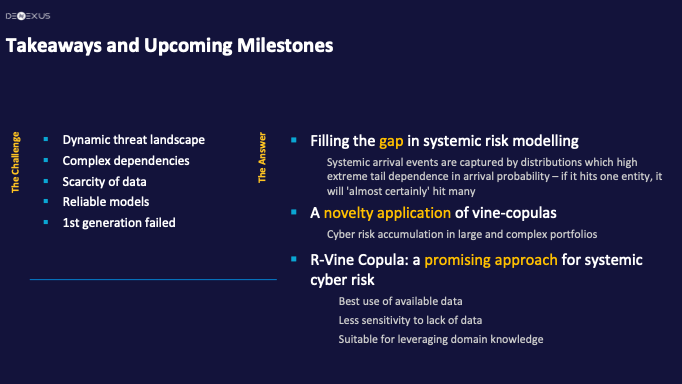
In conclusion, the R-vine based Co-Exposure model in DeRISK, informed by both facility attributes and their intricate correlation structures powered by inside-out data, emerges as a pioneering tool for addressing critical Cyber Risk Accumulation challenges, facilitating more informed decision-making in efficient cyber risk management, enabling event-based wordings in Cyber Insurance Policies.
Click Here to read more about the DeNexus Knowledge Center and the DeNexus Trusted EcoSystem.
Click Here to learn more about DeRISK, a comprehensive Cyber Risk Quantification and Management platform!<